First cells on ancient Earth may per chance per chance maybe merely have emerged because building blocks of proteins stabilized membranes.
Life on Earth arose about 4 billion years within the past when the important thing cells formed within a primordial soup of complex, carbon-well off chemical substances.
These cells faced a chemical conundrum. They wanted particular ions from the soup in state to carry out frequent choices. But these charged ions would have disrupted the simple membranes that encapsulated the cells.
A crew of researchers at the College of Washington has solved this puzzle the use of fully molecules that would have been unusual on the early Earth. The use of cell-sized, fluid-stuffed compartments surrounded by membranes made from fatty acid molecules, the crew chanced on that amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, can stabilize membranes in opposition to magnesium ions. Their results divulge the stage for the important thing cells to encode their genetic knowledge in RNA, a molecule related to DNA that requires magnesium for its production, while striking ahead the stability of the membrane.
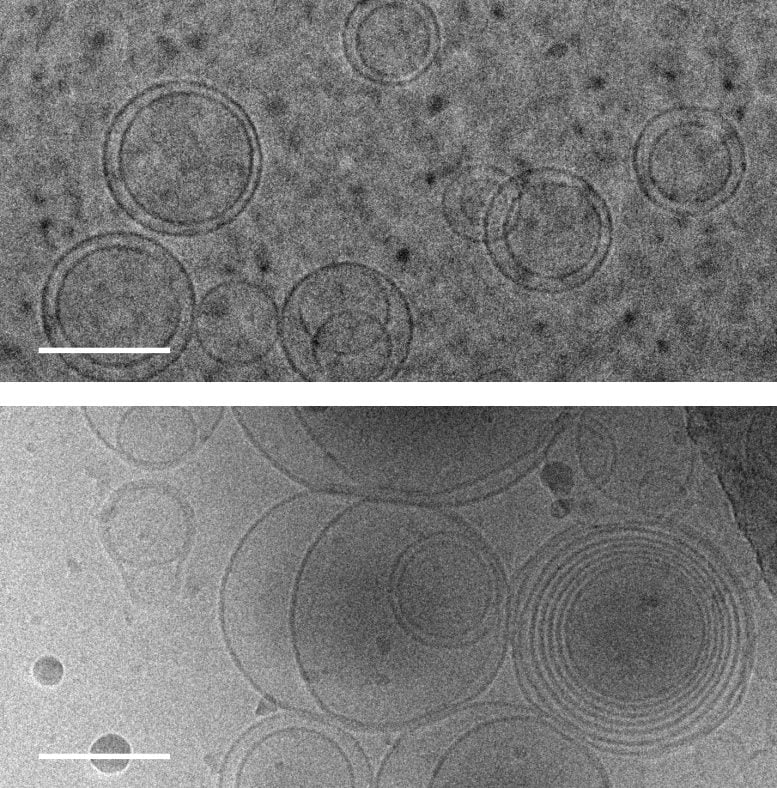
Photography of membranes (circles) taken the use of transmission electron cryomicroscopy. Top: membranes in a resolution that contains no amino acids. Bottom: membranes in a resolution containing serine, an amino acid, which triggers membranes to earn more than one layers of concentric membranes. Scale bars: 100 nanometers. Credit: Alex Mileant/Caitlin Cornell
The findings, published Aug. 12 within the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences, transcend explaining how amino acids may per chance per chance maybe have stabilized membranes in nasty environments. They furthermore shriek how the particular person building blocks of cellular constructions — membranes, proteins, and RNA — may per chance per chance maybe have co-localized within watery environments on the conventional Earth.
“Cells are made up of very a range of kinds of constructions with fully a range of kinds of building blocks, and it has never been sure why they'd attain collectively in a functional formulation,” said co-corresponding creator Roy Black, a UW affiliate professor of chemistry and bioengineering. “The thought was once right that — somehow per chance maybe — they did attain collectively.”
Black came to the UW after a profession at Amgen for the assorted to possess within the main, missing main factors within the relieve of that “somehow per chance maybe.” He teamed up with Sarah Keller, a UW professor of chemistry and an expert on membranes. Black had been impressed by the observation that fatty acid molecules can self-assemble to earn membranes, and hypothesized that these membranes may per chance per chance maybe act as an very neutral proper surface to assemble the building blocks of RNA and proteins.
“You may per chance well per chance maybe per chance also accept as true with a range of kinds of molecules transferring at some stage within the primordial soup as fuzzy tennis balls and laborious squash balls bouncing spherical in a gargantuan box that's being shaken,” said Keller, who is furthermore co-corresponding creator on the paper. “Whilst you happen to line one surface interior the box with Velcro, then fully the tennis balls will follow that surface, and they also may per chance per chance maybe end up shut collectively. Roy had the insight that native concentrations of molecules may per chance per chance maybe be enhanced by the same mechanism.”
The crew beforehand confirmed that the building blocks of RNA preferentially achieve to fatty acid membranes and, surprisingly, furthermore stabilize the soft membranes in opposition to detrimental effects of salt, a typical compound on Earth previous and unusual.
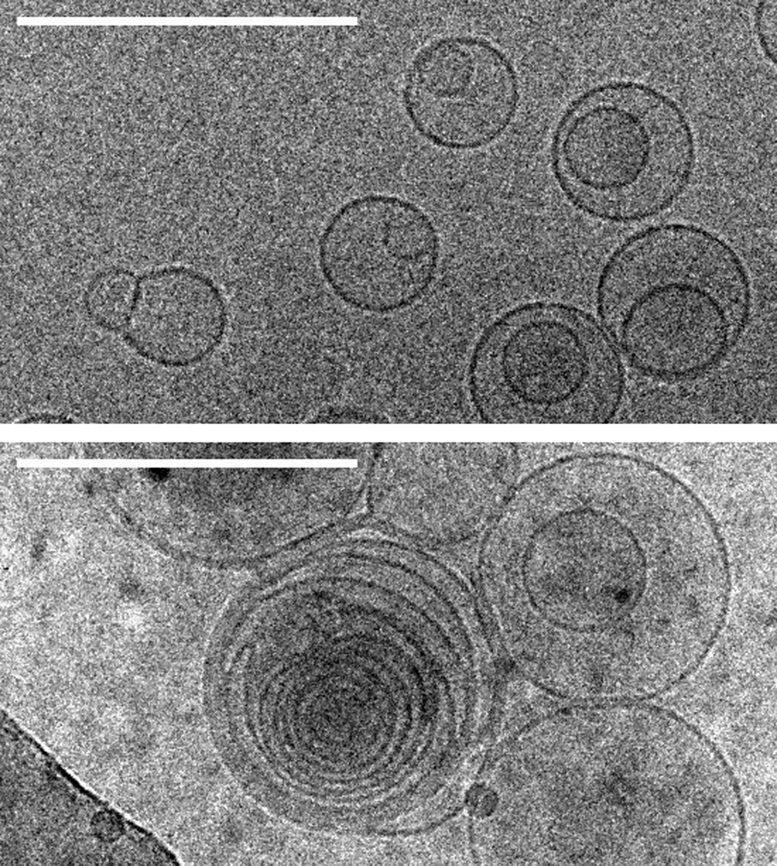
Photography of membranes (circles) taken the use of transmission electron cryomicroscopy. Top: membranes in a resolution of magnesium chloride, a salt that disrupts membranes, and no amino acids. Bottom: membranes in a resolution of magnesium chloride and serine, an amino acid, which triggers membranes to earn more than one layers of concentric membranes. Scale bars: 100 nanometers. Credit: Alex Mileant/Caitlin Cornell
The crew hypothesized that amino acids may per chance per chance maybe furthermore stabilize membranes. They worn a fluctuate of experimental ways — including gentle microscopy, electron microscopy and spectroscopy — to verify how 10 a range of amino acids interacted with membranes. Their experiments printed that definite amino acids bind to membranes and stabilize them. Some amino acids even brought about well-organized structural changes in membranes, comparable to forming concentric spheres of membranes — great fancy layers of an onion.
“Amino acids weren't right conserving vesicles from disruption by magnesium ions, but they furthermore created multilayered vesicles — fancy nested membranes,” said lead creator Caitlin Cornell, a UW doctoral pupil within the Division of Chemistry.
The researchers furthermore chanced on that amino acids stabilized membranes thru changes in focus. Some scientists have hypothesized that the important thing cells may per chance per chance maybe merely have formed within shallow basins that went thru cycles of high and low concentrations of amino acids as water evaporated and as unusual water washed in.
The unusual findings that amino acids defend membranes — to boot to prior results exhibiting that RNA building blocks can play the same role — stamp that membranes may per chance per chance maybe merely have been a location for these precursor molecules to co-localize, providing a doable mechanism to shriek what brought collectively the ingredients for lifestyles.

A model of how the building blocks of the important thing cells may per chance per chance maybe merely have co-localized on membranes. Left: the building blocks of membranes, RNA and proteins within the primordial soup. Middle: membranes earn (grey circle) and bind a subset of the building blocks, which in turn stabilize the membranes. Correct: functional RNA and proteins encased by the membrane. Credit: Roy Black/Sarah Keller
Keller, Black and their crew will turn their consideration subsequent to how co-localized building blocks did something a ways more grand: They sure to 1 one more to earn functional machines.
“That is the following step,” said Black.
Their ongoing efforts are furthermore forging ties all the map in which thru disciplines at the UW.
“The College of Washington is an surprisingly right space to fabricate discoveries thanks to the passion of the scientific community to work collaboratively to part instruments and tips all the map in which thru departments and fields,” said Keller. “Our collaborations with the Drobny Lab and the Lee Lab were main. No single laboratory may per chance per chance maybe have performed all of it.”
Co-authors are Gary Drobny, UW professor of chemistry; Kelly Lee, UW affiliate professor of medicinal chemistry; UW postdoctoral researchers Mengjun Xue and Helen Litz within the Division of Chemistry, and James Williams within the Division of Medicinal Chemistry; UW graduate college students Zachary Cohen within the Division of Chemistry and Alexander Mileant within the Biological Structure, Physics and Make Graduate Program; and UW undergraduate alumni Andrew Ramsay and Moshe Gordon. The evaluation was once funded by NASA, the Nationwide Institutes of Health and the Nationwide Science Basis.
View Source


0 Yorumlar